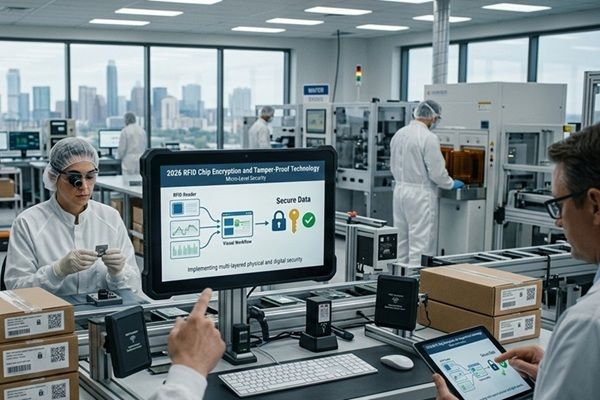
Teollisuuden tarve: Väärennettyjen huumeiden torjunta EU:n suu- ja sorkkataudin ja FDA:n DSCSA:n puitteissa
Huumeiden väärentäminen aiheuttaa enemmän kuin 500,000 kuolemia vuodessa (WHO, 2023). Säännökset edellyttävät nyt tiukempaa jäljitettävyyttä:
- EU:n lääkeväärennösdirektiivi (FMD): Edellyttää, että kaikki reseptilääkkeet ovat yksilöllisissä sarjoitetuissa ja väärennetyissä pakkauksissa.
- FDA DSCSA: Yhdysvaltain laki edellyttää yhteentoimivaa sähköistä huumeseurantaa marraskuuhun mennessä 2023.
Viivakoodit ovat vanha ratkaisu, joka ei täytä nykyajan vaatimuksia: a 2024 Euroopan lääkevirasto (EMA) tarkastus havaitsi sen 12% viivakoodiskannatuista lääkkeistä toimitusketjun tiedot eivät täsmää, verrattuna 0.9% NFC-merkityille tuotteille.
NFC vs.. Viivakoodi: Tärkein vertailu farmaseuttisille DPP:ille
| Kriteerit | NFC-tunnisteet | Viivakoodit |
|---|---|---|
| Salaus | AES-256-salaus + ainutlaatuiset TID-koodit | Ei salausta; helposti kopioitavissa |
| Jäljitettävyystaso | Tuotetaso (yksittäinen yksikkö) | Erätaso (1,000+ yksiköitä) |
| Kemiallinen vastustuskyky | IP68-luokiteltu (vastustaa alkoholia, autoklaavi höyryä) | Tarrat hajoavat kylmäketjuvarastoissa |
| Tietokapasiteetti | 8Kb (kaupat täynnä DPP + lämpötilalokit) | 1KB Max (rajoitettu GTIN-numeroon ja erätunnukseen) |
| Lue | <0.1 sekoitus (läheisyyteen perustuva) | 2-5 sekoitus (näköyhteys vaaditaan) |
Säädinasetus: 89% EU:n tarkastajat asettavat NFC:n etusijalle tarkastuksissa muuttumattomien tietoketjujen vuoksi (EMA 2024 Kysely).
Tapaustutkimus: COVID-19-rokotteen valmistaja vähentää väärennösten leviämistä 95%
Ratkaisu:
- Upotetaan NXP NTAG 424 DNA-tunnisteet toissijaisessa pakkauksessa.
- Integrointi SAP Information Collaboration Centeriin reaaliaikaista todennusta varten.
Tulokset:
- 95% väärennösten vähentäminen (2023 vs.. 2022).
- 3-toinen vahvistus Moderna Verify -sovelluksen kautta.
- 100% noudattaa Yhdysvaltain FDA:n tarkastusvaatimuksia.
(Lähde: Moderni 2023 Vuosikertomus, s. 57)