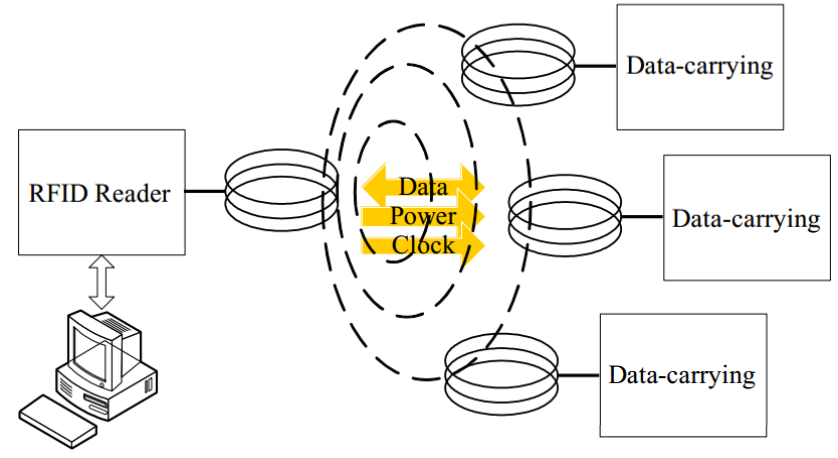
NFC Technology Introduction
NFC is a short-range, high-frequency wireless communication technology that allows contactless point-to-point data transmission between electronic devices, exchanging data over a distance of 10 centimetres. It integrates radio frequency identification technology and interconnection technology, which is convenient to operate, and is widely used in mobile payment, access control systems, electronic ticketing and other fields.
NFC tag working principle
NFC tags operate based on the principle of electromagnetic induction. When an NFC device, such as a mobile phone, is brought close to an NFC tag, the built-in antenna of the device generates an alternating magnetic field. The NFC tag also has an antenna coil, and when it is within this alternating magnetic field, according to the law of electromagnetic induction, the tag’s antenna coil generates an induced current, thereby powering the chip within the tag, allowing the chip to function.
NFC tag working procedure
Activation phase: The NFC reads that the device is turned on and its antenna generates an alternating magnetic field at a specific frequency (typically 13.56MHz). When the NFC tag enters this magnetic field range, the antenna inside the tag cuts the magnetic field lines, generating an induced electromotive force, which in turn generates a tiny current that activates the tag chip.
Data Transfer Preparation Phase: The activated tag chip starts working and prepares the data stored in the internal memory for transmission. The data storage structure of NFC tags is divided into different sectors and blocks, and each part can store different types of information, such as unique identification codes, application data, etc.
Data Transmission Phase: The tag changes the impedance of its antenna by modulating its own load, thus affecting the load on the antenna of the reading device. The reading device detects this change in load and parses out the data sent by the tag. Data transmission uses specific coding and modulation schemes, such as Manchester coding and ASK (Amplitude Shift Keying) modulation, to ensure accurate data transmission.
Data processing stage: After the reading device receives the data, it decodes and verifies it to ensure the integrity and accuracy of the data. After that, according to the application scenario, the data is transmitted to the upper-layer application for processing, such as verifying the payment information in the mobile payment and confirming the identity and authority in the access control system.
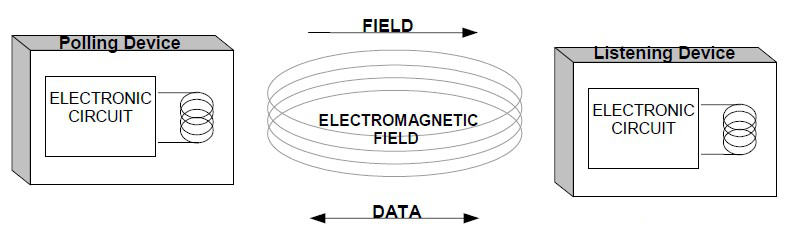
NFC tag types and Differences in working principles.
Passive NFC tags: They have no power supply and rely entirely on external magnetic fields for power, such as common NFC stickers. These tags are low-cost and compact, but they have a short working distance and relatively slow data transfer speeds.
Semi-active NFC tags: Combining the characteristics of passive and active, it is usually in a passive state with low power consumption, relying on external magnetic field power supply to maintain basic functions, and when data transmission is required, the built-in power supply is activated for active communication.
Summary
NFC tags communicate with reading devices through the principle of electromagnetic induction, and provide convenient data interaction services for various scenarios under the characteristics of different types of tags. As technology continues to evolve, NFC tags will play an important role in more fields and bring more convenience to our lives.
















